As businesses expand across borders and time zones, the need for continuous customer support team operations has become more critical than ever. The Follow-the-Sun (FTS) model offers a practical solution by distributing work across globally dispersed teams, enabling around the clock productivity.
Rather than pausing overnight, tasks move seamlessly from one region to another, accelerating delivery and improving responsiveness. This article explores how the FTS model works, its advantages, its challenges, and how organizations can assess whether it’s the right strategy for their needs.
What is the follow-the-sun model
The follow-the-sun model is a global workflow strategy commonly used in IT services, customer support, and software development. It leverages geographically dispersed multiple teams across multiple time zones to provide continuous service or productivity 24 hours a day.
The core idea behind the FTS model is to hand over tasks to the next team and knowledge sharing between multiple global locations, as one team's shift ends in one time zone and begins in another. This model is particularly valuable for:
- 24/7 technical support
- Global incident response
- Around-the-clock software development teams
- International customer service
For example, a software bug identified in the North American team at the end of the business day can be worked on by a team in India or Japan during their business hours, and then passed to a team in Europe, and finally back to the US.
Key benefits of using the follow-the-sun model
Adopting the Follow-the-Sun model can bring significant advantages to organizations with global operations. From faster response times to improved customer satisfaction, this approach offers practical value that extends beyond simple time zone coverage.
Faster turnaround times
By continuously passing tasks between global teams as each workday ends, organizations can eliminate the downtime associated with traditional, geographic location-based workflows. Instead of waiting until the next morning for work to resume, business operations continue seamlessly in the next time zone.
Enhance customer satisfaction
With different teams distributed around the world, customers can receive timely, localized support regardless of time zone differences. This eliminates the frustration of waiting for a support team’s business hours to begin and ensures that escalations or follow-ups don’t stall due to timezone delays.
Increased productivity
When teams hand off their tasks with maintained consistency in documentation and clear communication, their counterparts can immediately pick up where they left off. This continuous workflow reduces downtime and enhances the efficient use of global resources and continuous progress. It also enables parallel task execution — while one region codes a feature, another can simultaneously conduct testing or documentation.
Workload distribution and flexibility
By rotating responsibilities globally, the burden of critical tasks or urgent issues is not concentrated on a single team on the same project. This balance allows teams to work standard hours without the stress of night shifts or incurring overtime costs. It fosters a healthier work environment, encourages work-life balance, and can help reduce burnout.
Resilience and business continuity
Because work is not centralized in one location, disruptions in a specific region are less likely to halt operations entirely. The regular handoff of knowledge and responsibilities between teams also helps maintain momentum, even in challenging situations, shortening development duration. This geographic redundancy ensures that critical services remain operational, and businesses can proceed with problem-solving with minimal interruption.
Common challenges of using the follow-the-sun model and how to fix them
The follow-the-sun model, while powerful, introduces several operational and organizational challenges. Below is a detailed overview of the main challenges and practical solutions for each:
Ineffective handoffs
Inadequate documentation, vague task statuses, or missed context can lead to duplicated efforts, delays, and misunderstandings.
Solution:
Establish standardized, structured handoff protocols. Use collaborative tools like Jira, Confluence, or ServiceNow. Implement a checklist or template for handoffs to ensure consistent quality. If feasible, schedule brief synchronous overlap windows to discuss critical issues before the transition.
Lack of visibility and coordination
When teams are geographically dispersed with minimal time-zone overlap, they may lose sight of the overall project context or dependencies.
Solution:
Introduce centralized dashboards and shared progress tracking systems that give all teams visibility into current status, goals, and blockers. Maintain an always-accessible knowledge base and promote knowledge sharing. Appoint regional coordinators to act as communication bridges.
Cultural differences and communication barriers
Cultural differences, communication styles, and different languages can lead to misunderstandings or uneven collaboration across regions.
Solution:
Provide cross-cultural communication training and encourage inclusive practices. Use clear, simple, and unambiguous language in documentation and communication. Promote the use of common language tools and establish norms for responsiveness and tone.
Tool and process fragmentation
Multiple locations might use disparate tools, platforms, or processes, leading to inconsistencies in how work is tracked and handed off.
Solution:
Standardize the same tools and workflows across all locations. Choose integrated platforms that support real-time collaboration, automated updates, and seamless handoffs. Provide standardized processes in documentation and tool usage training.
Reduced sense of ownership
Because tasks are constantly handed off, individuals may feel disconnected from the end-to-end outcome.
Solution:
Create mechanisms for shared ownership, where teams are not just contributors but also stakeholders in outcomes. Use management information systems tied to collective success, not just regional KPIs.
Time zone gaps and lack of overlap
In some regions, the time zone gap may be so wide that there is no overlap at all, making real-time communication nearly impossible.
Solution:
For critical transitions, ensure at least 15–30 minutes of intentional overlap in working hours, even if that requires slight scheduling adjustments. For non-critical tasks, rely on asynchronous updates using video recordings, voice notes, and rich documentation.
Key principles in incorporating the follow-the-sun model
Implementing the FTS model successfully requires more than just distributing teams across time zones. It depends on clear processes, the right tools, and a collaborative mindset.
Establish clear and structured handover processes
Every shift transition should include a comprehensive knowledge transfer, with clear documentation of what has been done, what is pending, any blockers, and recommended next steps. Use structured templates or checklists to ensure consistency in handovers.
Best practices include:
- Maintaining a shared task tracker (e.g., Jira, Trello, Asana).
- Using handover logs that are reviewed and updated daily.
- Encouraging the team leads to highlight critical issues or nuances that might be lost in translation.
This structured handoff prevents misunderstandings and ensures work continues seamlessly from one region to the next.
Standardize tools and platforms across teams
Disparate tools and fragmented systems can derail coordination in follow-the-sun workflows.
Ensure all teams work within the same suite of collaboration tools, such as:
- Project management: Jira, ClickUp
- Communication: Slack, Microsoft Teams
- Documentation: Confluence, Notion
- Version control and CI/CD: GitHub, GitLab, Jenkins
Standardization makes it easier to train new team members, maintain visibility, and enforce consistent work practices. It also simplifies reporting and performance tracking across regions.
Implement overlap hours where possible
While the follow-the-sun model aims to minimize reliance on synchronous communication, small overlap periods, even just 15–30 minutes, can dramatically improve coordination.
These windows can be used to:
- Review ongoing work and handoffs.
- Clarify ambiguities in real-time.
- Discuss critical blockers or escalations.
Where overlap isn’t feasible, asynchronous communication tools or detailed issue trackers can help fill the gap, maximizing productivity.
Invest in documentation and knowledge management
High-quality documentation is essential in an asynchronous, distributed environment.
Each team should maintain up-to-date records on:
- System architectures and design decisions.
- Support runbooks and incident response protocols.
- Project plans and engineering roadmaps.
- Client interactions and support history.
Documentation should be written clearly and kept in a centralized, accessible location to avoid silos. Use tools like Confluence or Notion to keep this knowledge base organized and searchable.
Foster a collaborative and inclusive culture
To make follow-the-sun work and meet the customer demands, you need more than tools — you need trust, empathy, and a shared sense of purpose across time zones and cultures.
Encourage cross-regional engagement through:
- Regular global team meetings or town halls.
- Shared Slack channels for casual conversation and bonding.
- Rotational leadership or collaboration roles that give all regions visibility.
Cultural awareness training can also help teams understand and respect each other's communication styles, holidays, and time constraints.
Define clear roles, ownership, and accountability
Without direct oversight, it’s easy for responsibilities to become blurred.
Clearly define:
- Who owns which tasks.
- What "done" means for each team or region.
- How escalations should be handled.
Use RACI (responsible, accountable, consulted, informed) matrices or similar frameworks to ensure accountability is distributed and clear. This improves both autonomy and effectiveness.
Use metrics to monitor and improve the model
Continuous improvement requires data.
Track and analyze metrics such as:
- Task completion times across shifts.
- Incident resolution SLAs.
- Handoff quality (like frequency of rework or missed context).
- Team satisfaction and engagement.
Use retrospectives or feedback loops to refine handover procedures and team coordination regularly. Encourage regions to share what’s working well and where friction remains.
Plan for business continuity and redundancy
Finally, treat the follow-the-sun model as a core part of your business continuity strategy. Ensure that if one region is suddenly offline due to a power outage, political issue, or natural disaster, another region can take over with minimal disruption.
Maintain:
- Redundant infrastructure across locations.
- Shadow teams that can quickly be activated.
- Global software engineering workshops so key skills are not siloed in one region.
This practice not only boosts reliability but also strengthens resilience during crises.
How LiveChat helps incorporate the follow-the-sun model
LiveChat offers a suite of features that can support companies implementing an FTS model, especially in the context of 24/7 customer support and distributed team collaboration. Its tools enable organizations to provide continuous, seamless customer service across different time zones with continuous integration implemented correctly across all channels.
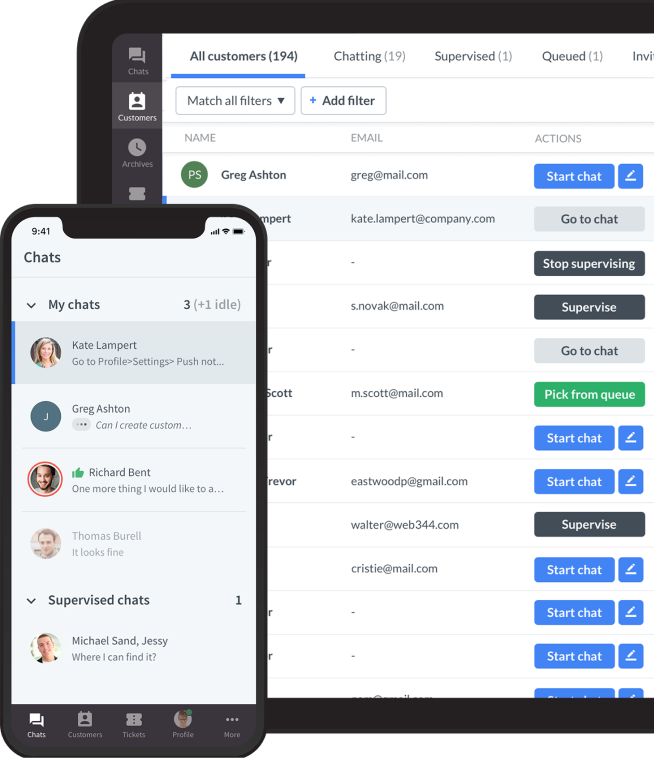
24/7 live chat capability
LiveChat enables real-time chat interactions, and teams in different regions can staff them around the clock. Businesses can assign agents from various time zones to ensure someone is always available to respond to customer inquiries.

Follow-the-sun benefit:
Supports continuous customer service coverage, allowing handovers between regional teams without downtime.
Chat routing and agent grouping
LiveChat allows businesses to route chats based on availability, department, or geography. You can set up agent groups by region (for example, Asia, Europe, the Americas) and route chats accordingly.

Follow-the-sun benefit:
Enables region-specific handoffs and optimized workload distribution, key to follow-the-sun efficiency.
Automated greetings and triggers
Using automated greetings and behavior-based triggers, LiveChat ensures that customer interactions are acknowledged instantly, even if no human agent is immediately available. This can include welcome messages, queuing info, or directing users to self-service options.

Follow-the-sun benefit:
Maintains responsiveness during handover gaps and enhances customer experience during shift changes.
Chatbots and AI automation
LiveChat integrates with chatbots through its ChatBot platform, enabling automated responses for FAQs, order status, or triage before escalating to a human agent.

Follow-the-sun benefit:
Bridges gaps in coverage or overlap hours, especially when transitioning between shifts or covering low-activity regions.
Agent availability scheduling
Admins can manage agent schedules and availability statuses, helping coordinate shift coverage across global teams.

Follow-the-sun benefit:
Supports effective team scheduling and ensures agents are aligned with their designated time zones for proper handoff.
Multilingual support
LiveChat supports multiple languages in both the agent interface and customer chat widget, allowing businesses to cater to a diverse, global audience.

Follow-the-sun benefit:
Improves regional service personalization and reduces communication barriers between international teams and customers.
Integrations with CRMs and help desk tools
LiveChat integrates with platforms like HelpDesk, Salesforce, HubSpot, Zendesk, and others. This ensures that customer data, conversation history, and unresolved tickets are accessible across time zones.

Follow-the-sun benefit:
Provides context continuity and helps agents in different regions pick up conversations without losing valuable background information.
Real-time monitoring and analytics
Managers can track active chats, agent activity, and performance metrics across all time zones in real-time.

Follow-the-sun benefit:
Enables global oversight, performance benchmarking across regions, and identification of weak points in the handover process.
Mobile and desktop apps
LiveChat offers apps for Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android, allowing agents to stay connected and handle customer issues from anywhere.
Follow-the-sun benefit:
Enhances workforce flexibility and ensures coverage during transitional or hybrid work hours.
Sample follow-the-sun model shift plan using LiveChat
| Region | Time zone | Coverage hours | Example locations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asia-Pacific | GMT +8 to +10 | 8:00 AM to 4:00 PM APAC | Manila, Sydney, Tokyo |
| Europe/Middle East/Africa (EMEA) | GMT +1 to +3 | 8:00 AM to 4:00 PM EMEA | Warsaw, Berlin, Cape Town |
| Americas | GMT -8 to -5 | 8:00 AM to 4:00 PM AMER | New York, Toronto, Bogotá |
Shift coverage
Shift 1: APAC Team (8:00 AM – 4:00 PM GMT+8)
Key responsibilities:
- Begin daily support cycle.
- Handle overnight tickets from the EMEA and AMER regions.
- Update CRM and LiveChat ticket notes for visibility.
LiveChat features in use:
- Agent grouping: “APAC Support Team” for chat routing.
- Chat routing rules: Automatically direct chats from Asia-Pacific users to this team.
- CRM integration: Update Salesforce or HubSpot with conversation logs.
Shift 2: EMEA Team (8:00 AM – 4:00 PM GMT+1)
Key responsibilities:
- Pick up handovers from the APAC region.
- Manage European traffic volume.
- Triage and escalate any global issues unresolved by APAC.
LiveChat features in use:
- Automated handover notes: LiveChat custom fields and tags to track transition status.
- Live monitoring: Supervisors monitor APAC logs and ticket queues.
- Multilingual widgets: Localized LiveChat UI for French, German, and Polish customers.
Shift 3: Americas Team (8:00 AM – 4:00 PM GMT-5)
Key responsibilities:
- Close out the day’s customer support cycle.
- Finalize resolutions or log pending issues for APAC.
- Prepare asynchronous summaries for the APAC team.
LiveChat features in use:
- ChatBot automation: During EMEA/AMER overlap, bots triage inquiries and handle FAQs.
- Tags and transcripts: Used to flag follow-ups or unresolved chats.
- Mobile App Support: Remote agents respond during flexible hours if needed.
Asynchronous automation bridge
When teams are transitioning between shifts (for instance, 30–60 minute gap windows), LiveChat’s automation suite ensures continuity:
- ChatBot handles routine issues, captures intent, and creates tickets.
- Triggers and greetings inform customers of estimated wait times or regional availability.
- Fallback routing ensures overflow chats are queued with clear expectations.
Does the follow-the-sun model work for you
Determining whether a company should adopt the FTS model requires a strategic evaluation of its operational demands, customer expectations, and global reach.
| Criterion | If you answer "Yes"... |
|---|---|
| Global customer base | You likely need round-the-clock coverage |
| Strict SLAs or 24/7 expectations | Follow-the-sun may be essential |
| Urgent, time-sensitive issue resolution | Continuous handoffs improve response |
| High volume of support or ops tasks | Enables balanced workload distribution |
| Teams in multiple regions/time zones | Natural fit for follow-the-sun scheduling |
| Strong async tooling and documentation | Youâre ready for seamless handoffs |
Global customer base and time zone distribution
Ask: Do we serve customers across multiple continents or time zones?
Indicators:
- High volume of support requests or sales queries after local business hours.
- Frequent service-level agreement (SLA) violations due to time constraints.
- Complaints about delayed issue resolution in non-headquarters regions.
Service expectations and SLA requirements
Ask: Are we contractually or competitively required to provide 24/7 service or fast response times?
Indicators:
- Critical systems or products with guaranteed uptime (99.9% SLA).
- Customer contracts with global support clauses.
- Dependence on real-time troubleshooting or technical escalation.
Nature and urgency of support needs
Ask: What is the impact of delaying support, resolution, or delivery by several hours?
Indicators:
- Outages, bugs, or incidents must be addressed immediately.
- Continuous deployment or agile workflows that can't pause overnight.
- DevOps or support teams struggle to manage after-hours escalations.
Operational complexity and task volume
Ask: Is there enough work or global collaboration to justify 24-hour operations?
Indicators:
- Backlogs of support tickets or unresolved tasks that span days.
- Frequent need to continue or escalate work across time zones.
- Current teams are overwhelmed during peak hours but idle at other times.
Existing or planned global team structure
Ask: Do we already have or plan to build international offices or distributed teams?
Indicators:
- Existing operations in APAC, EMEA, and the Americas.
- Plans to expand support, engineering, or sales in other countries.
- A globally remote workforce that could be structured around time zones.
Tooling and process readiness
Ask: Do we have the tools and processes in place to support asynchronous work and smooth handoffs?
Indicators:
- Use of tools like Slack, Jira, Confluence, Zendesk, or LiveChat.
- Standardized documentation and onboarding processes.
- Handoff protocols are already informally in place.
When FTS may not be necessary
- Your customers are located in one region/time zone.
- You operate in a 9-to-5, low-urgency environment.
- Most support tasks can wait until the next business day.
- You lack the resources to build and manage regional teams.
Final thoughts
The follow-the-sun model is a strategic framework for driving global software development with efficiency and responsiveness. When implemented thoughtfully, it allows teams to collaborate across time zones, reduce turnaround times, and maintain consistent service standards regardless of location.
But it also demands the right tools, processes, and cultural alignment to succeed. For organizations operating on a global scale or aiming to meet rising expectations for speed and availability, the FTS model offers a clear path toward continuous, coordinated, and scalable operations.